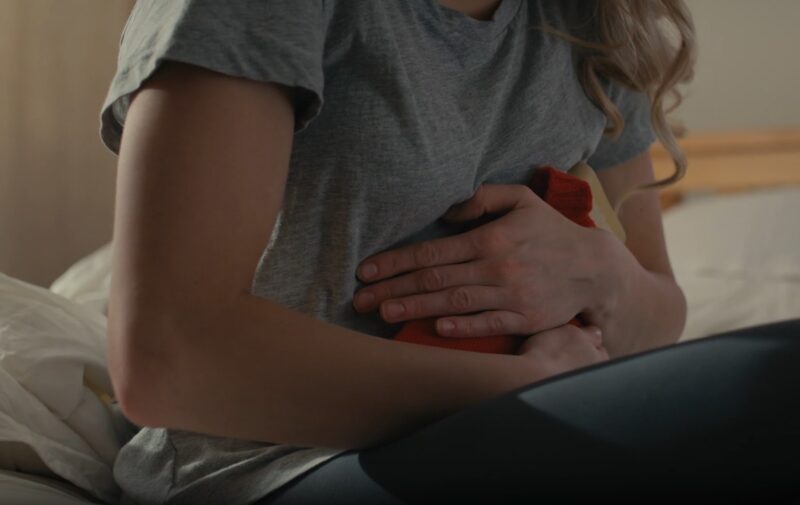
Identifying the source of abdominal pain is crucial for proper treatment. Both the gallbladder and liver play vital roles in digestion and metabolism.
Let us take a look at the differences between these two.
Differentiating Between Gallbladder and Liver Pain
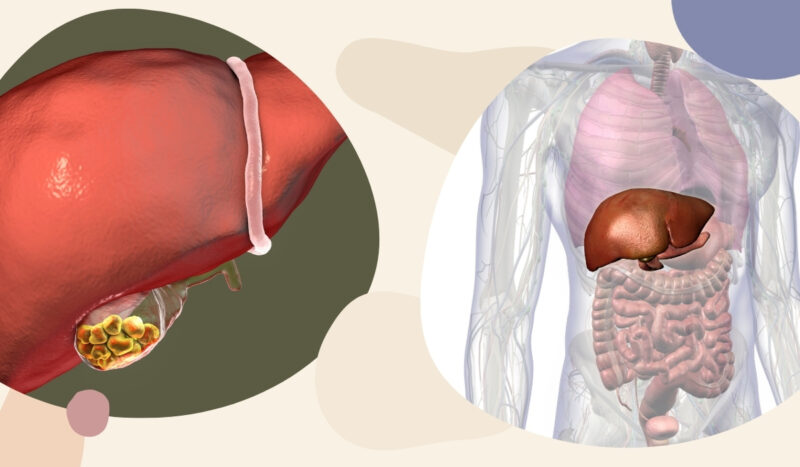
Before we go deep into the characteristics of these two, we want to talk about what separates them.
Pain Characteristics and Location
Gallbladder pain is typically sharp and intense, often triggered by eating fatty foods and radiating to the shoulder or back.
In contrast, liver pain tends to be a dull, constant ache associated with inflammation or infection.
Associated Symptoms
Gallbladder issues are often accompanied by fever, chills, vomiting, jaundice, and pale stools.
Liver problems, on the other hand, are more likely to present with fatigue, weakness, dark urine, and jaundice.
Trigger Factors
Gallbladder pain is commonly triggered by consuming fatty foods or certain body positions that stress the gallbladder.
Liver pain can be exacerbated by alcohol consumption and the intake of specific medications that affect liver function.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Problems
Symptoms of gallbladder problems are quite numerous, but the most common ones are:
Pain Location and Nature
Gallbladder issues typically present with pain in the upper-right abdomen, which may radiate to the back and right shoulder.
This pain often intensifies after consuming fatty foods.
Associated symptoms include: Gallbladder problems can arise from conditions such as:
Pain due to gallstones is sudden and sharp, while cholecystitis pain can be more persistent and severe.
Gallbladder Diseases and Complications
Gallstones form when substances in bile, such as cholesterol or bilirubin, harden. These stones can block bile ducts, causing significant pain and infection.
There are two main types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol stones
- Pigment stones
Cholecystitis, an inflammation of the gallbladder, can be acute or chronic and is often caused by gallstones obstructing the bile ducts.
Other complications include porcelain gallbladder, which involves calcium deposits in the gallbladder wall, bile duct stones, abscesses, ileus (intestinal blockage), polyps, and cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing gallbladder issues typically involves imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, and cholescintigraphy, as well as endoscopic procedures like ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography).
Treatment options range from surgical interventions, such as cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal), to antibiotics for infections, natural remedies, and dietary adjustments to reduce fat intake.
Symptoms of Liver Problems
Now, we want to address the commonest liver problems.
Pain Location and Nature
Liver-related pain generally manifests as a dull ache or pressure in the upper-right abdomen. This discomfort may be accompanied by:
Conditions affecting the liver include hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and complications from gallstones, pancreatitis, or muscle strain.
Pain from liver issues can worsen with alcohol consumption and certain medications.
Liver Diseases and Complications
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by viral infections (hepatitis A, B, C, D, E) or other factors like alcohol and toxins.
Symptoms include jaundice, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
Cirrhosis, characterized by liver scarring, results from chronic liver disease and leads to liver dysfunction.
Liver cancer may arise from chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis and presents symptoms like weight loss, loss of appetite, and jaundice.
Other complications include infections, gallstones that impact liver function, and conditions like muscle strain or pancreatitis affecting liver performance.
Diagnosis and Treatment
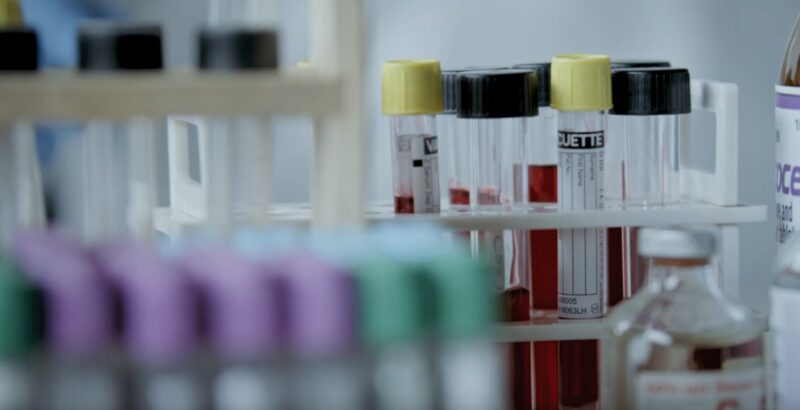

Liver problems are diagnosed through blood tests (liver function tests), imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI), and liver biopsy to assess liver tissue.
Treatment depends on the underlying condition and may involve antiviral medications for hepatitis, lifestyle changes to manage cirrhosis, surgery for liver cancer, and in severe cases, liver transplantation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience severe or persistent abdominal pain, jaundice, high fever with chills, or sudden weight loss.
Early diagnosis and treatment of gallbladder and liver conditions are crucial to prevent complications.
Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist, worsen, or significantly impact daily life.
Related Posts:
- Can You Keep Your Wisdom Teeth? Here’s What Dentists Say
- How Stress and Anxiety Can Lead to Gastritis - What…
- Can Hernias Affect Your Back? 9 Key Facts to Know
- How an MSN Degree Can Enhance Your Career After an ADN?
- 7 Signs Your Hernia Pain Needs Immediate Attention
- Top 14 Home Remedies for Relieving Pain in the Anus