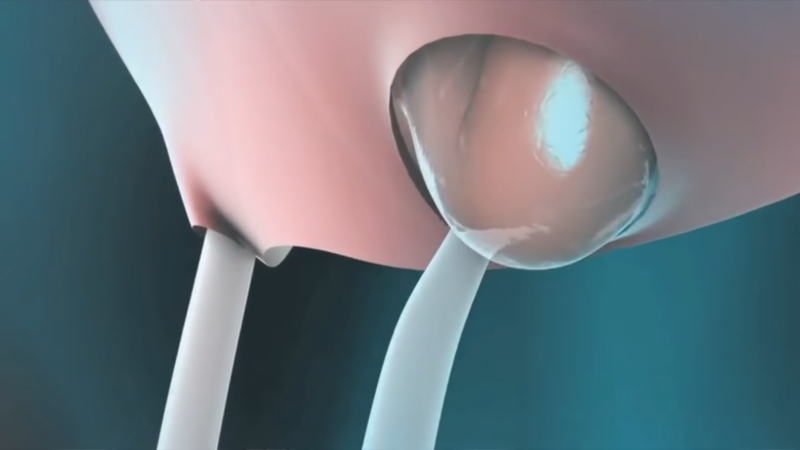
Hernia pain can range from mildly uncomfortable to severely debilitating. While some discomfort is normal, certain signs indicate the need for immediate medical attention. Recognizing these symptoms early can prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
Here are seven critical signs that your hernia pain requires urgent care.
- Severe or persistent pain
- A sudden increase in pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever
- Changes in bowel movements
- Redness or discoloration at the site
- Swelling that doesn’t reduce
1. Severe or Persistent Pain
Why Severe Pain is a Red Flag
Severe pain that doesn’t subside with rest or over-the-counter pain medications can indicate a complication. One of the most concerning issues is a strangulated hernia, a condition where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off. This can lead to tissue death if not treated promptly and is considered a medical emergency.
Identifying Strangulated Hernias
A strangulated hernia presents with intense, unrelenting pain and can be accompanied by symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and fever. The affected area might also show signs of discoloration or become very tender to touch. Immediate intervention is necessary to restore blood flow and prevent severe complications.
Other Potential Complications
2. Sudden Increase in Pain

A sudden increase in pain in the area of your hernia can be a clear indication that something is wrong and requires prompt medical attention. Understanding the significance and potential causes of this symptom is essential.
Why a Sudden Increase in Pain is Concerning
A rapid escalation in pain levels, especially after physical activity, lifting heavy objects, or even simple movements, may indicate a worsening condition. Such a pain spike could signify the development of a strangulated hernia or incarceration, both of which need urgent medical intervention.
Strangulated Hernia Concerns
A sudden increase in pain can be a sign of a strangulated hernia, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is abruptly cut off. This condition leads to tissue death if not addressed promptly. Along with severe pain, you might experience other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fever, and changes in skin color over the hernia site.
Incarcerated Hernia Indicators
Another possibility is that the hernia has become incarcerated, meaning it is trapped and cannot be pushed back into place. This situation can cause a sudden and significant increase in pain, along with symptoms like bowel obstruction, constipation, and an inability to pass gas.
3. Nausea or Vomiting

Why Nausea or Vomiting is Alarming
Nausea and vomiting, when associated with hernia pain, are significant red flags. These symptoms can suggest an intestinal blockage or a strangulated hernia, both of which are medical emergencies.
Intestinal Blockage Signs
Nausea and vomiting might also indicate an intestinal blockage, where the hernia obstructs the passage of food or stool. This blockage can lead to a buildup of pressure and pain, accompanied by the inability to pass gas or have a bowel movement, and often requires surgical intervention.
4. Fever
Why Fever is Concerning
A fever indicates the presence of an infection or inflammation in the body. When it accompanies hernia pain, it could signify a serious complication such as a strangulated hernia or an incarcerated hernia with infection.
Incarcerated Hernia and Infection
An incarcerated hernia, where the hernia is trapped and cannot be pushed back in, can also lead to infection. The trapped tissue can become inflamed, causing a fever as the body responds to the infection. This condition often presents with symptoms such as swelling, redness, and increased pain.
5. Changes in Bowel Movements
Why Changes in Bowel Movements Matter
Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation, inability to pass gas, or other irregularities, can suggest that the hernia is causing an intestinal obstruction. This condition occurs when the hernia impedes the normal flow of the intestines, leading to serious complications.
Intestinal Obstruction Indicators
An intestinal obstruction caused by a hernia can lead to symptoms such as severe pain, bloating, and a noticeable decrease in bowel movements. If the bowel becomes obstructed, it can result in a buildup of waste and pressure, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
6. Redness or Discoloration at the Site
Why Redness or Discoloration is Concerning
Redness or discoloration at the hernia site often indicates inflammation or infection. These symptoms can propose that the hernia is becoming more complicated, potentially leading to a strangulated hernia or other severe issues.
Signs of Infection
Infection at the hernia site can also cause redness, warmth, and swelling. This may occur if the hernia becomes incarcerated or if the tissue within the hernia sac becomes inflamed. Infections require prompt medical treatment to prevent the spread of bacteria and further complications.
7. Swelling That Doesn’t Reduce
Why Persistent Swelling is Concerning
Swelling that does not go down or becomes more pronounced can indicate complications such as an incarcerated hernia or a strangulated hernia. Both conditions require urgent medical care to prevent further health issues.
Incarcerated Hernia Indicators
An incarcerated hernia occurs when the herniated tissue becomes trapped and cannot be pushed back into the abdomen. This can lead to persistent swelling and increased pain at the site. If left untreated, an incarcerated hernia can result in an intestinal blockage or strangulation.
FAQs
How can I prevent hernia pain from worsening?
To prevent hernia pain from worsening, avoid heavy lifting, straining, or any activities that put pressure on the affected area. Wearing a supportive brace and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of complications.
What are the common risk factors for developing a hernia?
Common risk factors include chronic coughing, heavy lifting, obesity, pregnancy, and a family history of hernias. Age and previous surgeries in the abdominal area can also increase the likelihood of developing a hernia.
Can lifestyle changes help manage hernia pain?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as eating a high-fiber diet to avoid constipation, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight can help manage hernia pain and prevent complications.
When should I see a doctor about my hernia?
You should see a doctor if you notice any changes in your hernia, such as increased pain, swelling, redness, or if you experience symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel movements. Regular check-ups can help monitor the hernia and prevent serious complications.
Are there non-surgical treatments for hernia pain?
Non-surgical treatments may include lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and wearing a supportive truss or brace. However, these treatments are typically only temporary solutions, and surgery is often required to repair the hernia permanently.
What should I expect during hernia surgery recovery?
Recovery from hernia surgery typically involves rest, avoiding strenuous activities, and following your doctor’s post-operative instructions. Most people can return to normal activities within a few weeks, but complete recovery may take longer, depending on the severity of the hernia and the type of surgery performed.