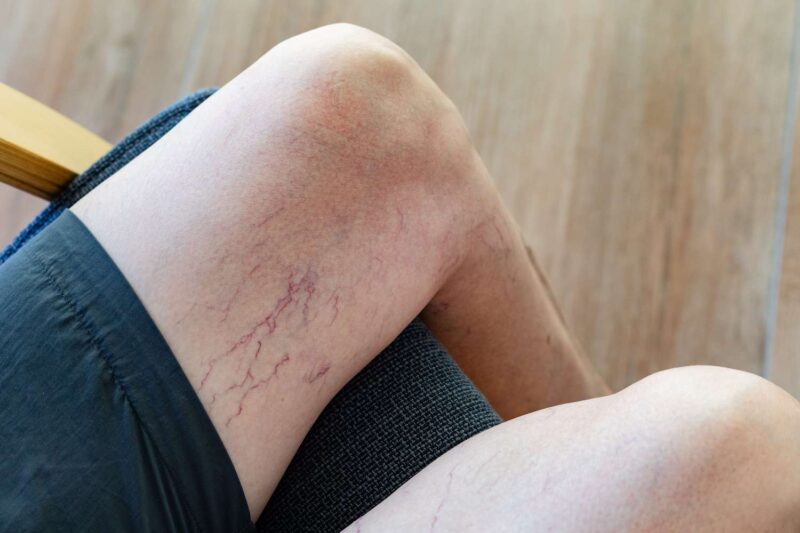
A burst vein in your leg, often associated with varicose veins, can cause significant discomfort and health risks. Understanding the causes and recognizing the symptoms early are crucial for effective management.
Factors such as increased blood pressure within the veins, physical trauma, weakened vein walls, obesity, and prolonged periods of standing or sitting can contribute to vein ruptures. Identifying a burst vein involves noticing signs like swelling, pain, discoloration, and bleeding.
This guide explores the underlying causes and offers practical insights on recognizing and addressing this condition promptly.
These Are the Main Causes of Vein to Burst
- Increased Blood Pressure
- Physical Trauma
- Weakened Vein Walls
- Obesity
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Increased Blood Pressure
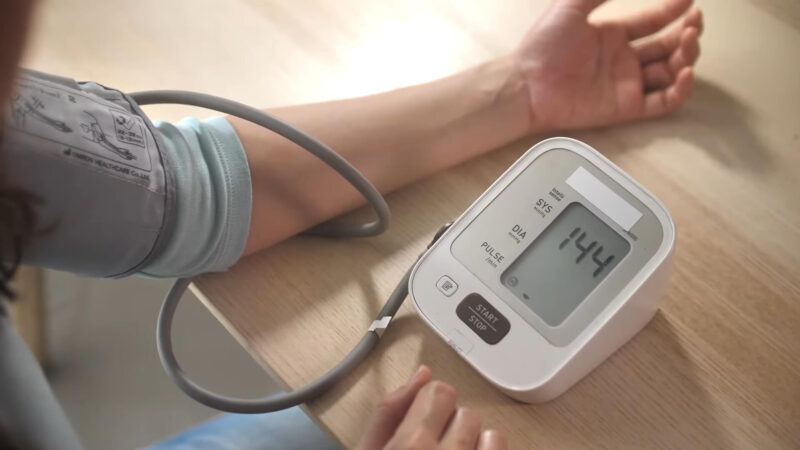
High blood pressure within the veins, often referred to as venous hypertension, is a primary cause of vein ruptures. This condition occurs when the pressure inside the veins exceeds normal levels, placing excessive force on the vein walls. Over time, this persistent pressure can weaken the structural integrity of the veins, making them more susceptible to ruptures.
How It Happens
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI): This condition involves the malfunction of vein valves, which are responsible for ensuring one-way blood flow back to the heart. When these valves fail, blood pools in the veins, causing increased internal pressure. This pooling effect is often exacerbated by prolonged standing or sitting, as gravity hinders blood flow from the lower extremities to the heart.
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases the amount of blood circulating through the veins and raises the pressure within them. The added weight also puts physical pressure on the veins, further contributing to venous hypertension.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of movement can lead to poor circulation and increased pressure within the veins. Regular muscle contractions during physical activity help pump blood through the veins, reducing the risk of pressure build-up.
Symptoms and Risks
- Swelling: Increased pressure in the veins often leads to swelling in the legs, as fluids leak from the veins into surrounding tissues.
- Pain and Discomfort: The pressure can cause aching or a heavy feeling in the legs, which may worsen after long periods of standing or sitting.
- Visible Vein Changes: The veins may become more prominent, bulging, and twisted, indicating high internal pressure.
Prevention
- Compression Stockings: These help reduce pressure by supporting the vein walls and improving blood flow.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity promotes circulation and helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels within the veins.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the veins, lowering the risk of venous hypertension and subsequent ruptures.
Physical Trauma

Physical trauma to the leg can cause a vein to burst. This occurs when an external force, such as a blow or impact, damages the vein walls. Physical trauma is a common cause of vein rupture, particularly in active individuals or those involved in accidents.
How It Happens
- Direct Impact: A sudden blow to the leg from sports activities, falls, or accidents can directly damage the veins. The impact force can cause the vein walls to tear or burst.
- Pressure from External Objects: Situations where the leg is compressed or pinched, such as being caught in machinery or trapped under heavy objects, can lead to vein rupture due to the extreme pressure applied.
- Repetitive Strain: Repeated minor injuries or continuous strain on the veins, common in certain sports or physical jobs, can weaken the veins over time, making them more susceptible to bursting.
Symptoms and Risks
- Visible Bruising: The most common symptom of a burst vein due to trauma is bruising around the affected area. The bruise results from blood leaking out of the damaged vein into the surrounding tissue.
- Swelling and Pain: Swelling and localized pain often accompany bruising, as the body responds to the injury.
- Immediate Bleeding: In severe cases, especially if the skin is broken, there may be visible bleeding from the burst vein. This bleeding can be significant and may require immediate medical attention.
Prevention and Management
- Protective Gear: Using appropriate protective gear during sports and physical activities can help prevent trauma to the legs.
- Safe Practices: Adopting safe practices in physical work environments and during exercise can minimize the risk of leg injuries.
- Immediate Care: If a vein bursts due to trauma, apply pressure to the area to control bleeding, elevate the leg, and seek medical attention to prevent complications.
Weakened Vein Walls
Weakened vein walls are a common vascular problem that can lead to significant health complications if left untreated. Over time, the structural integrity of veins can deteriorate due to aging, health conditions, and lifestyle factors.
When vein walls become fragile, they are more prone to bursting, leading to varicose veins, swelling, and pain. Understanding the underlying causes and addressing them early can help improve vein health and prevent more severe complications.
How It Happens
Now let us see how it happens.
Aging
As people age, the natural elasticity and strength of vein walls decline. Veins are lined with muscle fibers and connective tissue that allow them to stretch and contract as blood flows through them.
Over time, these fibers weaken, and the walls become thinner and less capable of handling pressure.
When the walls lose their flexibility, they are more likely to rupture under stress, such as increased blood pressure or prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) is a condition where the valves inside the veins fail to function properly. Veins have one-way valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves weaken or become damaged, blood pools in the veins, creating increased pressure against the vein walls.
This persistent pressure causes the veins to stretch and weaken over time, making them more susceptible to rupture.
CVI is a progressive condition, meaning that without treatment, the damage will worsen, increasing the risk of complications such as ulcers and blood clots.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions directly affect vein health and contribute to weakened vein walls.
- Diabetes – High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and reduce the body’s ability to repair tissue. This leads to poor circulation and weakened veins.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) – Increased pressure in the circulatory system puts constant strain on vein walls, causing them to thicken and weaken over time.
- Cardiovascular Disease – Poor heart function reduces blood flow, causing the veins to work harder to return blood to the heart.
Genetic Factors
Genetics also play a significant role in vein health. Some individuals inherit weaker connective tissue or dysfunctional vein valves, which increases their susceptibility to varicose veins and other vascular problems.
If a family history of vein disease exists, proactive measures such as wearing compression stockings and maintaining an active lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing weakened veins.
Symptoms and Risks
Weakened vein walls can lead to a range of visible and physical symptoms that signal underlying vascular issues.
- Varicose Veins – One of the most common symptoms of weakened veins is the development of varicose veins. These twisted, enlarged veins are often visible under the skin, particularly in the legs. Varicose veins result from poor blood flow and increased pressure, which cause the veins to bulge and become more fragile.
- Swelling and Pain – Poor blood circulation due to weakened veins can lead to swelling, heaviness, and discomfort in the legs. This discomfort often worsens after standing or sitting for extended periods.
- Skin Changes – When veins weaken, blood flow to the skin becomes compromised. This can cause the skin around the affected veins to become discolored, thin, and prone to ulcers. Severe cases may lead to open sores that are difficult to heal due to poor circulation.
- Bleeding and Rupture – In extreme cases, weakened vein walls can rupture, leading to bruising or bleeding under the skin. If a varicose vein bursts, immediate medical attention may be required to prevent further complications.
Prevention
Preventing vein wall weakening involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments. Strengthening vein walls and improving circulation can reduce the risk of complications.
Compression Stockings
Wearing compression stockings is one of the most effective ways to support weakened vein walls. Compression stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, promoting blood flow and reducing swelling. They help veins maintain their shape and function, preventing further weakening and reducing the risk of rupture.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can improve overall vascular health and prevent vein problems.
- Exercise Regularly – Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and cycling help strengthen veins and improve blood circulation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight – Excess body weight increases pressure on the veins, particularly in the lower body. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces this strain.
- Balanced Diet – Eating foods high in fiber, antioxidants, and vitamins supports vein health and reduces inflammation. Reducing sodium intake also helps prevent fluid retention, which can increase pressure on vein walls.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing – Sitting or standing for long periods reduces blood flow and increases pressure in the veins. Taking breaks to walk or stretch can help prevent vein damage.
Medical Treatment
For individuals with significant vein wall weakening or varicose veins, medical treatments may be necessary.
- Sclerotherapy – A non-surgical procedure where a solution is injected into damaged veins, causing them to collapse and fade.
- Laser Therapy – A minimally invasive treatment that uses laser energy to close off damaged veins, redirecting blood flow to healthier veins.
- Vein Stripping or Ligation – Surgical procedures that involve removing or tying off damaged veins to prevent further complications.
If you need to schedule an appointment to check up on your veins and consult with a vein specialist., visit rosenveincare.com.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Ignoring symptoms of weakened veins can lead to more severe issues, including chronic swelling, skin ulcers, and thrombosis (blood clots). If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or changes in skin color around the veins, it’s important to seek medical advice. Early treatment improves outcomes and helps maintain vein function.
Strengthening vein walls and addressing health conditions that contribute to vein weakening can significantly reduce the risk of complications. Taking preventative measures and seeking professional care when needed ensures better vascular health and improved overall well-being.
Obesity

Obesity is a significant risk factor for vein ruptures due to the increased strain it places on the circulatory system. Excess body weight can exacerbate venous pressure, contributing to the weakening of vein walls and the formation of varicose veins, which are prone to bursting.
How It Happens
- Increased Venous Pressure: Excess weight adds pressure to the veins, particularly in the lower extremities. This heightened pressure can weaken vein walls over time, making them more susceptible to ruptures.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI): Obesity is closely linked with CVI, where vein valves do not function correctly, causing blood to pool in the veins and increasing internal pressure. This pooling effect stretches and weakens the veins.
- Inflammation and Poor Circulation: Obesity often leads to systemic inflammation and poor blood circulation. These conditions can damage the veins, reducing their elasticity and strength.
Symptoms and Risks
- Varicose Veins: Individuals with obesity are more likely to develop varicose veins, which are enlarged, twisted veins that can rupture under increased pressure.
- Swelling: Obesity can cause swelling in the legs due to poor circulation and increased pressure within the veins. This swelling can signal underlying vein issues.
- Pain and Discomfort: The additional weight can lead to aching, throbbing, and discomfort in the legs, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting

Extended periods of standing or sitting can contribute significantly to vein ruptures, especially in individuals predisposed to venous insufficiency. The lack of movement impedes proper blood flow, increasing pressure within the veins and leading to potential ruptures.
How It Happens
- Impaired Blood Flow: When you stand or sit for long durations without moving, the blood flow in your legs slows down. This lack of movement means the muscles in your legs are not contracting enough to help push blood back to the heart, causing blood to pool in the veins.
- Increased Venous Pressure: Prolonged immobility increases the pressure within the veins. This pressure can weaken the vein walls over time, leading to bulging veins that are more prone to ruptures.
Symptoms and Risks
- Swelling and Edema: Swelling in the legs and ankles is a common symptom of prolonged immobility. This swelling results from fluid buildup due to poor venous return.
- Pain and Discomfort: Individuals may experience aching, heaviness, or throbbing in the legs, particularly after extended periods of standing or sitting.
- Visible Varicose Veins: Prolonged immobility can exacerbate varicose veins, making them more prominent and increasing the risk of rupture.
Recognizing a Burst Vein
Recognizing a burst vein in the leg is crucial for seeking timely medical intervention and preventing complications. The symptoms of a burst vein can vary based on whether the rupture is internal or external, but several key signs can help identify this condition.
Symptoms to Watch For
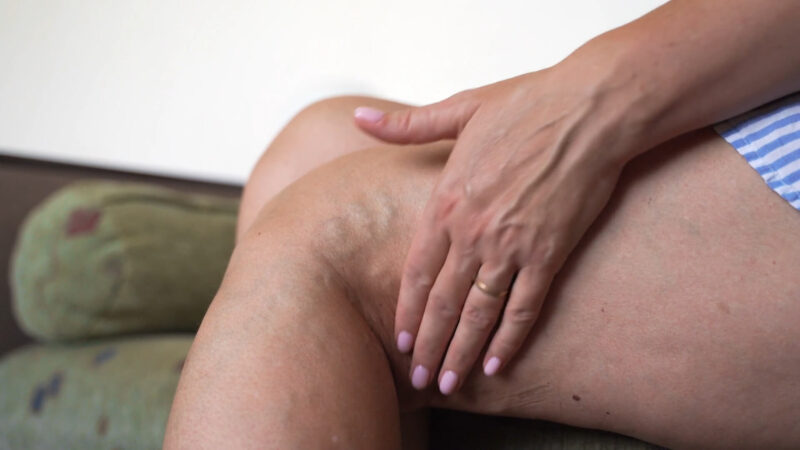

- Swelling: Localized swelling around the affected area is a common symptom of a burst vein. The swelling may fluctuate in intensity and is usually accompanied by other symptoms such as pain or discomfort.
- Discoloration: A burst vein can cause visible discoloration of the skin. This often appears as bruising, with the skin turning purple or blue due to blood leaking from the ruptured vein into surrounding tissues.
- Pain or Throbbing: Persistent pain or a throbbing sensation in the leg is a typical symptom of a burst vein. This pain may intensify with movement or pressure applied to the area.
- Bleeding: In cases where the skin is broken, significant bleeding can occur. This bleeding may be rapid and profuse, requiring immediate medical attention to prevent excessive blood loss.
- Visible Bulging Veins: Prior to bursting, varicose veins may appear more prominent and bulging. If these veins are accompanied by the symptoms mentioned above, it could indicate a high risk of rupture.
Internal vs. External Rupture
- Internal Rupture: When a vein bursts internally without breaking the skin, symptoms include bruising, swelling, and potentially dizziness or fainting due to blood pooling inside the leg. Immediate medical attention is necessary to avoid complications from blood clots or severe internal bleeding.
- External Rupture: When the vein bursts and breaks through the skin, it results in external bleeding. This bleeding can be substantial and requires immediate steps to control blood flow and seek medical help.
Immediate Actions to Take
- Apply Pressure: Use a clean cloth or bandage to apply direct pressure to the area to control bleeding.
- Elevate the Leg: Raise the leg above heart level to reduce swelling and blood flow to the area.
- Seek Medical Help: Contact a healthcare provider or visit an emergency room promptly to address the rupture and prevent further complications.
FAQs
What are the long-term effects of a burst vein if left untreated?
Untreated burst veins can lead to several long-term complications. These include chronic pain, persistent swelling, and the development of leg ulcers. Over time, the compromised veins can cause skin changes, such as discoloration and thickening, which may increase the risk of skin infections. In severe cases, untreated burst veins can result in deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, potentially leading to life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent vein ruptures?
Yes, lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of vein ruptures. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting, and wearing compression stockings can all help improve vein health. Additionally, quitting smoking and eating a balanced diet rich in fiber can support vascular health and prevent the weakening of vein walls.
How can pregnancy affect the risk of vein ruptures?
Pregnancy can increase the risk of vein ruptures due to several factors. The increased blood volume needed to support the growing fetus puts additional pressure on the veins. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also relax the vein walls, making them more susceptible to varicose veins and potential ruptures. Additionally, the weight of the growing baby can put extra pressure on the veins in the lower extremities.
Are there any surgical options for treating severe vein ruptures?
For severe cases of vein ruptures or chronic varicose veins, surgical options are available. These include vein stripping, where the affected vein is removed, and endovenous thermal ablation, which uses heat to close off damaged veins. Another option is sclerotherapy, where a solution is injected into the vein to collapse it. These procedures are typically performed by a vascular surgeon and may require a recovery period, but they can effectively reduce symptoms and prevent future ruptures.
What role do genetics play in the likelihood of experiencing a burst vein?
Genetics can play a significant role in the likelihood of developing varicose veins and experiencing vein ruptures. If you have a family history of varicose veins or chronic venous insufficiency, you are at a higher risk of developing these conditions yourself. Genetic factors can influence the strength and elasticity of your vein walls and valves, making them more susceptible to damage and increasing the risk of vein-related issues.
Last Words
Understanding the causes and symptoms of a burst vein in your leg is crucial for effective management and prevention. Recognizing symptoms like swelling, pain, discoloration, and bleeding can help you take prompt action.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking appropriate medical treatment can significantly reduce the risk of vein ruptures and ensure better vascular health. Taking these steps can help prevent complications and promote overall well-being.