Ambulatory surgery, widely recognized as outpatient surgery, signifies a groundbreaking shift in healthcare, enabling patients to receive specific surgical procedures without requiring an overnight stay in a hospital. This forward-thinking model has significantly altered the terrain of surgical care, providing a more convenient, cost-effective, and efficient option compared to the traditional approach of inpatient surgeries.
In the broader context of global health, the International Association for Ambulatory Surgery (IAAS) plays a crucial role in the last sentence of this evolution, championing the adoption and standardization of ambulatory surgery practices worldwide.
The Rise
The concept of ambulatory surgery has gained significant traction over the past few decades, primarily due to advancements in medical technology and anesthesia. These developments have made it possible to perform a wide range of surgeries – from minor procedures to more complex operations – in a safe and efficient manner, without the need for prolonged hospitalization.
Key Benefits
One of the most notable benefits of ambulatory surgery is the convenience it offers to patients. By eliminating the need for an overnight stay, patients can return to the comfort of their homes on the same day of the surgery, which can significantly reduce the stress and disruption often associated with traditional surgical procedures.
Additionally, ambulatory surgery centers often provide a more personalized and streamlined experience, with shorter wait times and a focus on patient-centered care.
Types of Procedures Suitable
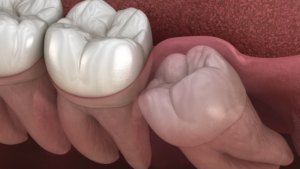
Many minor surgical procedures are ideally suited for ambulatory settings. These include but are not limited to, minor dermatological procedures, cataract surgery, and certain dental surgeries.
These procedures typically involve minimal incisions, reduced risk of complications, and a quick recovery time, making them perfect candidates for outpatient surgery.
Intermediate Complexity Procedures
With advancements in surgical techniques and anesthesia, a growing number of procedures of intermediate complexity are now being performed on an outpatient basis. Examples include arthroscopic surgeries, hernia repairs, and some cosmetic surgeries.
These procedures, while more complex than minor surgeries, can still be safely performed in an ambulatory setting with the right preparation and post-operative care.
Advanced Procedures
In some cases, even more advanced surgeries can be performed as ambulatory procedures. This is particularly true in specialties like orthopedics and gynecology, where surgeries such as joint replacements and hysterectomies are increasingly being done on an outpatient basis.
These procedures require meticulous planning and coordination, as well as thorough patient selection to ensure safety and efficacy.
Advancements in Technology and Anesthesia
The evolution of medical technology has played a pivotal role in the expansion of ambulatory surgery. Minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy and robotic surgery, have significantly reduced the invasiveness of many procedures.
These technologies result in smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery times, making them ideal for outpatient settings.
Anesthesia Developments
Advancements in anesthesia have been equally crucial in the growth of ambulatory surgery. The development of short-acting anesthetics and improved pain management protocols have greatly enhanced patient comfort and safety.
These anesthetic techniques allow for quick recovery of consciousness and mobility, enabling patients to go home shortly after their procedures.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
Effective preoperative and postoperative care is essential in ambulatory surgery. This includes thorough patient education, careful screening for suitability, and meticulous planning of the surgical procedure.
Postoperatively, patients receive detailed instructions for at-home care and are typically followed up closely to ensure a smooth and complication-free recovery.
Patient Selection Criteria
Not every patient or procedure is suitable for ambulatory surgery. The selection process is a critical aspect, involving a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, current health status, and the nature of the proposed surgery.
Factors such as age, underlying medical conditions, and the patient’s support system at home play a crucial role in determining eligibility for outpatient surgery.
Importance of Preoperative Screening
Preoperative screening is vital to ensure patient safety and the success of the surgery. This screening often includes laboratory tests, medical evaluations, and sometimes consultations with specialists.
The goal is to identify any potential risks that could complicate the surgery or the recovery process, thereby ensuring that only those patients who are likely to have a safe and successful outcome are selected.
Role of Patient Education
Educating patients about the procedure, what to expect, and how to care for themselves postoperatively is an integral part of the ambulatory surgery process. Informed patients are more likely to follow postoperative instructions, recognize signs of complications, and participate actively in their recovery, all of which contribute to better outcomes.
Economic and Social Implications

One of the most significant advantages of ambulatory surgery is its cost-effectiveness. By reducing or eliminating the need for overnight hospital stays, these procedures can significantly lower healthcare costs.
This is beneficial not only for patients but also for healthcare systems and insurers, as it helps to reduce the financial burden on the entire system.
Impact on Healthcare Accessibility
Ambulatory surgery can also enhance healthcare accessibility. By freeing up hospital beds and resources, more patients can receive timely surgical care.
This is particularly important in areas with limited healthcare resources or long waiting lists for certain procedures.
Social Benefits
From a social perspective, ambulatory surgery allows patients to recover in the comfort of their own homes, reducing the emotional and psychological stress associated with hospital stays. This approach also minimizes disruption to patients’ lives, as they can return to their normal activities, including work and family responsibilities, more quickly.
The Future

The field of ambulatory surgery is continuously evolving, with new technologies and surgical techniques expanding the range of procedures that can be performed on an outpatient basis. Telemedicine and remote monitoring are also becoming increasingly important, allowing for better postoperative care and follow-up in the patient’s home.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its many benefits, ambulatory surgery faces challenges, including ensuring patient safety, managing complications, and maintaining high-quality standards. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and improvement, driving the field toward even greater efficiency and effectiveness.
The Role of Research and Development
Ongoing research and development are crucial for the future of ambulatory surgery. This includes not only advancements in medical technology and anesthesia but also in areas like patient education, preoperative assessment, and postoperative care.
As the field continues to grow, these efforts will help ensure that ambulatory surgery remains a safe, effective, and patient-centered option for an ever-expanding range of surgical procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the criteria for a patient to be considered suitable?
Suitability for ambulatory surgery depends on several factors, including the patient’s overall health, the complexity of the surgery, age, underlying medical conditions, and the availability of a support system at home. A comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history and current health status is essential to determine eligibility.
How do advancements in anesthesia contribute to its success?
The development of short-acting anesthetics and improved pain management protocols has been crucial. These advancements allow for quicker recovery of consciousness and mobility, enabling patients to go home shortly after their procedures, thereby making ambulatory surgery more feasible and safe.
Can complex surgeries like joint replacements be performed?
Yes, with advancements in surgical techniques and patient care, even complex surgeries like joint replacements can be performed on an outpatient basis. However, this requires meticulous planning, coordination, and thorough patient selection to ensure safety and efficacy.
What role does patient education play?
Patient education is vital in ambulatory surgery. It involves informing patients about the procedure, what to expect during recovery, and how to care for themselves postoperatively. Educated patients are more likely to follow instructions, recognize signs of complications, and actively participate in their recovery, leading to better outcomes.
How does it impact healthcare costs and accessibility?
Ambulatory surgery can significantly lower healthcare costs by reducing or eliminating the need for overnight hospital stays. It also enhances healthcare accessibility by freeing up hospital beds and resources, allowing more patients to receive timely surgical care, especially in areas with limited healthcare resources.
What are the challenges faced, and how are they addressed?
Challenges include ensuring patient safety, managing complications, and maintaining high-quality standards. Addressing these challenges involves continuous innovation, improvement in medical technology, anesthesia, patient education, preoperative assessment, and postoperative care. Ongoing research and development are also crucial to address these challenges effectively.
Final Words
Ambulatory surgery, a modern medical breakthrough, has transformed surgical care by allowing various procedures without an overnight hospital stay, enhancing healthcare efficiency and patient experience. This approach, driven by advancements in medical technology and anesthesia, has expanded the range of surgeries performed outside hospitals, from minor to complex operations.
Its benefits include convenience, cost-effectiveness, and minimal life disruption, reducing stress for patients and financial strain on healthcare systems. Success depends on careful patient selection and education.
With continuous innovation and telemedicine integration, ambulatory surgery is set to become even more central in healthcare, exemplifying patient-centered care and aligning with contemporary needs.
Related Posts:
- The Risks of Back Surgery - What You Need to Know…
- Top 13 Healthcare Jobs That Don’t Know You Need Experience
- Direct Hernia vs. Indirect Hernia: What You Need to Know
- What’s Behind Gluten Sensitivity? 10 Causes You Need to Know
- Common Colonoscopy Questions: What You Need to Know
- How Stress and Anxiety Can Lead to Gastritis - What…